Cybersecurity attacks are a growing concern for organizations around the world, with insider threats being a significant contributor to data breaches. In a recent study, it was found that a staggering 60% of data breaches are caused by insiders. These breaches initiated by malicious insiders have proven to be the most costly, with an average cost of USD 4.90 million, 9.5% higher than the average data breach cost. In this article, we will explore the percentage of cybersecurity attacks executed by insiders, the impact of these attacks on organizations, and strategies for mitigating the risks associated with insider threats. By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of the prevalence of insider threats and the steps that can be taken to protect against them.
Understanding Insider Threats in Cybersecurity
Insider threats in cybersecurity refer to security threats that originate from authorized users, such as employees, contractors, and business partners, who misuse their legitimate access intentionally or accidentally, or have their accounts hijacked by cybercriminals. Malicious insiders are disgruntled employees or former employees who misuse their access for revenge or financial gain, while negligent insiders create security threats through ignorance or carelessness. Compromised insiders are legitimate users whose credentials have been stolen by outside threat actors.
These insider threats can be especially costly and dangerous, with data breaches initiated by malicious insiders being the most costly, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023. To better detect, contain, and prevent insider threats, security teams rely on practices and technologies such as employee and user training, identity and access management, user behavior analytics, and offensive security measures.
Examples of insider threats in cybersecurity
Examples of insider threats in cybersecurity include a disgruntled former employee of a medical packing company using a previously created admin account to disrupt the shipment of personal protective equipment to hospitals during the COVID-19 pandemic, and a Twitter employee arrested for sending private information to officials of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in exchange for bribes. Negligent insiders, who do not have malicious intent, are responsible for a majority of insider threats, often resulting from carelessness or falling for phishing attacks. Compromised insiders, on the other hand, are legitimate users whose credentials have been stolen by outside threat actors.
To combat these insider threats, security teams rely on a combination of practices and technologies such as employee training, identity and access management, user behavior analytics, and offensive security measures, including phishing simulations and red teaming.
The Prevalence of Insider Threats
Statistics on the percentage of cybersecurity attacks executed by insiders
Insider threats are a significant concern in cybersecurity, as they can originate from authorized users who intentionally or accidentally misuse their access. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, data breaches initiated by malicious insiders were the most costly, with an average cost of USD 4.90 million. Additionally, incidents involving an insider threat actor have resulted in exposure of 1 billion records or more, as reported by Verizon. Malicious insiders, negligent insiders, and compromised insiders are the three types of insider threats, each with their own specific characteristics and potential impact. It takes security teams an average of 85 days to detect and contain an insider threat, making it challenging to separate careless or malicious insider threat indicators from regular user actions and behaviors.
Types of Insider Threats
- Malicious insiders
- Negligent insiders
- Compromised insiders
To address insider threats, security teams rely on a combination of practices and technologies, including employee and user training, identity and access management, user behavior analytics, and offensive security measures such as phishing simulations and red teaming.
Comparison of insider threats to external threats
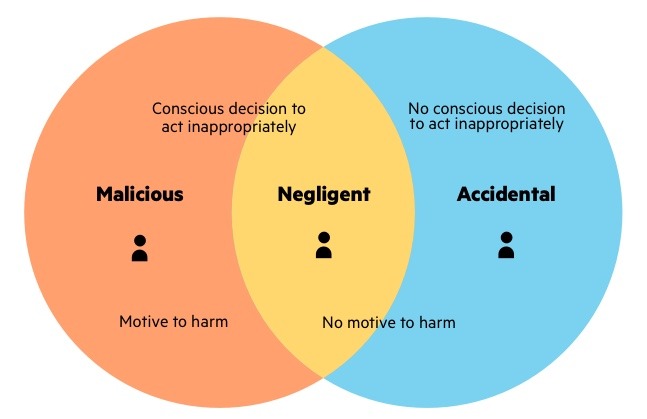
Insider threats pose a significant risk to organizations, as they can be more costly and dangerous than external threats. The majority of insider threats—56 percent—result from careless or negligent insiders, as reported by the 2022 Ponemon Cost of Insider Threats Global Report. Training all authorized users on security policy and security awareness can help lower the risk of negligent insider threats and blunt the impact of threats overall. Identity and access management (IAM) plays a crucial role in managing user identities, authentication, and access permissions to prevent insider attacks. User behavior analytics (UBA) applies advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence to detect abnormalities that can indicate emerging or ongoing cyberthreats, including potential insider threats. Offensive security tactics, such as phishing simulations and red teaming, can help strengthen insider threat programs. Overall, the detection and containment of insider threats is a complex challenge for security teams, and it requires a multi-faceted approach that combines training, technology, and proactive security measures to effectively mitigate the risk of insider threats.
Role of HR in Combating Insider Threats
- Assessing security policies
- Screening new hires
- Monitoring for disgruntled employees
- Providing regular cybersecurity awareness training
Mitigating Insider Threats
Insider threats, whether malicious or negligent, pose a significant risk to organizations, as highlighted by the high costs and potential dangers associated with such breaches. Malicious insiders, such as disgruntled employees or individuals working for outside entities, intentionally misuse their access for personal gain, while negligent insiders create security threats through ignorance or carelessness. Compromised insiders, whose credentials have been stolen by outside threat actors, also contribute to the costly and damaging nature of insider threats. It is clear that insider threats can result in significant financial and reputational damage to organizations, making it crucial for security teams to effectively detect and prevent such threats.
Implementing access controls and monitoring
Implementing access controls and monitoring allows organizations to closely monitor user activities and identify any unauthorized or suspicious behavior. By establishing strict access controls, organizations can limit the exposure of sensitive data and systems to only authorized personnel. Monitoring user activities in real-time helps in identifying any unusual behavior that may indicate a potential insider threat. Access controls and monitoring are critical components of an effective insider threat mitigation strategy.
Creating a culture of security awareness
Creating a culture of security awareness involves continuously training all authorized users on security policy and awareness to lower the risk of negligent insider threats. This can be achieved through regular cybersecurity awareness training programs that educate employees about best practices for data security, the importance of identifying and reporting suspicious activities, and the potential consequences of insider threats. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can empower their employees to actively participate in the protection of sensitive information.
Utilizing insider threat detection tools
Utilizing insider threat detection tools, such as user behavior analytics and offensive security measures, helps security teams to detect abnormal behaviors and strengthen network security against potential insider threats. User behavior analytics involve the use of machine learning algorithms to identify patterns of behavior that deviate from the norm, enabling early detection of insider threats. Offensive security measures, such as penetration testing and red team exercises, proactively assess an organization’s security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by insider threats.
Conclusion
Overall, mitigating insider threats requires a multifaceted approach that combines employee training, identity and access management, user behavior analytics, and offensive security measures. By implementing these practices and technologies, organizations can significantly improve their ability to detect, contain, and prevent insider threats, ultimately reducing the potential financial and reputational impact of such breaches.
conclusion
In conclusion, insider threats in cybersecurity are a pervasive and significant concern for organizations, with a majority of data breaches being attributed to authorized users. Whether intentional or accidental, insider threats can have a substantial financial impact on businesses, as well as legal and compliance ramifications. Mitigating this risk requires a multi-faceted approach that includes regular cybersecurity awareness training, proactive security measures, and the implementation of technology solutions. By educating employees about best practices for data security and the potential consequences o